数据结构回顾
1.1说到数据结构先谈谈什么是数据
1.数据:是描述客观事物的符号,是计算机中可操控的对象,能被计算机识别.并输入给计算机处理的符号集合.数据不光光包含整型,实型等数值类型,还包含音频,视频图像等等非数值类型.
2.数据元素:是组成数据的,有一定的基本单位 好比面向编程里面的一个个实体类 Person Bird
3.数据项:一个数据元素可以是若干个数据项组成,比如上面说的人有脚手鼻子眼睛换成编程中类的属性
4.数据对象:是性质相同的数据元素的集合,是数据的子集,好比人都有姓名,生日,性别相同的数据项
1.2那什么是结构呢?
大话数据结构里说:数据结构就是相互之间存在一种或者多种特定关系的数据元素的集合
我的认为就是用于储存很多数据元素的集合 好比java当中的数组或者list
并且把数据结构分成逻辑结构和物理结构
1.2.1首先说说这个逻辑结构
逻辑结构:是指数据对象中数据元素之间的相互关系. 分为一下四种
1.集合结构:集合结构中的数据元素除了同属于一个集合外,它们之间没有其他关系.
我的理解就是一个集合里塞了很多数据元素 比如一个广场上有3个人 他们彼此都不认识,他们仅仅就是在同一个广场上而已

2.线性结构:线性结构中的数据元素是一一对应的关系

3.树形结构:树形结构数据元素存在一种一对多的关系

4.图形结构:图形结构中的元素是多对多的

1.2.1再来说说这个物理结构
物理结构:是指数据的逻辑结构在计算机中的存储形式
数据元素的存储结构形式有两种:顺序存储和链式存储
1.顺序存储结构:是把数据元素存在放在连续的存储单元中,从编程语言的角度上就是数组,当你使用java
如上面的代码new了一个长度为4的int类型的数据 这个时候内存里就会为这个数据开辟4个连续的内存地址
2.链式存储结构:是把数据元素存放在任意的存储单位里,存储单元可以是连续的可以是不连续的,数据元素的存储关系并不能反应其逻辑关系,所以需要用一个指针存放数据元素的地址
2. 线性表==>零个或者多个数据元素的有限序列
2.1 线性表的顺序存储结构
线性表的顺序存储结构,指的是用一段地址连续的存储单位一次存储线性表的数据元素
要理解的话可以参考数据的原理
2.2 线性表的链式存储结构
真如1.2.1所说的链式存储结构 存储地址不是连续的 他们通过一个指针来标记他的前后
这里可以分成 单链表,静态链表,循环链表,双向链表
2.3 单链表==>
使用java实现单链表的基本功能
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
| package com.faith.datastruct;
public class LinkListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkList list = new LinkList();
list.add(1);
list.add(1);
list.add(1);
list.showNode();
System.out.println("=========");
LinkList list1 = new LinkList();
list1.add(2);
list1.add(2);
list1.add(2);
list1.showNode();
System.out.println("=========");
list.mergeNode(list1);
list.showNode();
}
}
class LinkList{
public Node head = new Node();
public void add(int value){
Node temp = head;
while (true){
if (temp.next == null){
temp.next = new Node(value);
return;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
public void showNode(){
Node temp = head.next;
if (temp == null){
System.out.println("链表为null");
return;
}
while (true){
if (temp == null){
break;
}
System.out.printf("val=%d,hashCode=",temp.data);
System.out.println(temp.hashCode());
temp = temp.next;
}
}
public void removeIndex(int index){
if (index < 0 || index > Count()){
System.out.println("请输入正确的下标");
}
if (index == 0 ){
head.next = head.next.next;
}
int i = 0;
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null){
if (i != index){
temp = temp.next;
i++;
}
else {
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}
}
}
public int Count(){
int count =0;
Node temp = head.next;
while (temp!=null){
count++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return count;
}
public boolean Contains(int key){
Node temp = head.next;
while (temp != null){
if (temp.data == key){
return true;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return false;
}
public void headAdd(int val){
Node temp = head;
if (temp.next == null){
head.next = new Node(val);
}else {
Node ins = new Node(val);
ins.next = head.next;
head.next = ins;
}
}
public void clear(){
head.next = null;
}
public Node gethead(){
return head;
}
public void mergeNode(LinkList list){
if (head.next == null){
head.next = list.gethead().next;
}
Node temp = head.next;
while (true){
if (temp.next == null){
temp.next = list.gethead().next;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
class Node{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(){
data = 0;
}
public Node(int val){
data = val;
}
}
|
2.4 静态链表
像C语言他有了指针这个东西,使得它可以非常容易的操纵内存中的地址和数据,后续的java c#虽然没有指针,但是一样有对象引用的概念,从一定角度也是实现了指针的功能
但是像一些早期的语言 他没有指针如何实现单链表呢
其实这个可以用数组的概念来实现
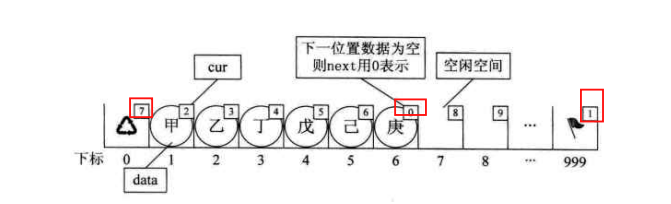
首先我们让数组的元素有两个数据域组成,cur和data,data就用来防止数据元素的数据,cur用来存放它下一个指向值得下标,cur就好比单链表中得next指针
我们把这种用数组表示的叫做静态链表,这种描述方法还有起名叫游标实现法

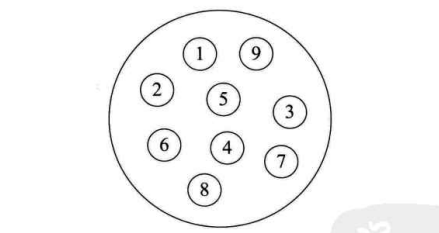
如图上
数组的第一个和最后一个属于是备用链表
第一个存储的是没有使用的数组元素的开始位置(比如数组长度10但是只塞了3个 那么这三个存储就是从静态数链下标为1开始存储 第一个存储的就是下标4 从4之后还有6个位置 减去最后一个还有5个位置)
最后一个存储的是数组存储数据的开始下标也就是从1开始存储 最后一个存储的cur就是1
2.5 循环链表
可以理解为单链表最后的节点的next指向第一个节点,这种头尾衔接起来的就可以称为循环链表
2.6 双链表
这个和前面的单链表的区别就是 双链表不仅仅指向它后面的节点还指向了它前面的节点
2.7 队列和栈
先来说说栈吧
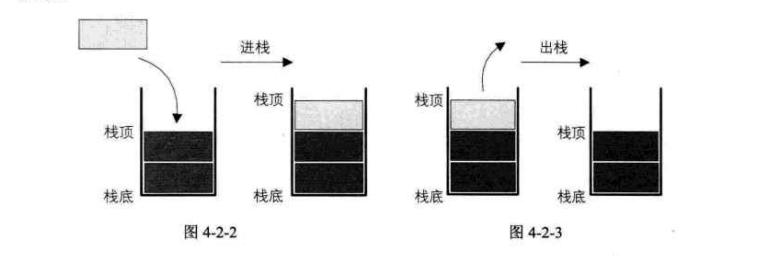
栈(stack) 是限定仅在表尾进行插入和删除的线性表,先进后出是他的特点

这里插一个中缀表达式合后缀表达式
实例
中缀表达式也就是我们平时看的懂得表达式 9 + (3 + 1) * 3 + 10 / 2
后缀表达式就是计算机能懂得表达式 9 3 1 - 3 * + 10 2 / +
再来看看这两个东西怎么转换??
规则
从左到右边 是数字就输出 是符号就入栈 当括号闭合得时候 输出括号内得符号 当栈内加入一个符号他前面得符号优先级比自己高得时候 把该符号前面到栈顶得符号出栈输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
|
再来说说队列
队列(queue)是只允许在一端进行插入操作 而在另一边进行删除操作得线性表
队列是一种先进先出得线性表允许插入的为一头是队尾 允许删除的为另外一头是队头
假设队列是q={a1,a2,a3,a4} 那么队头是a1 队尾是a4 因为a4后面a5 才是往里头插入的
3 串
串是由零个或者多个字符组成的有限序列
4 树
4.1、为什么需要用到树形结构
4.1.1、数组存储方式的分析
- 优点:通过下标方式访问元素,速度快。对于有序数组,还可以使用二分查找提高检索速度
- 缺点:如果要检索具体某个值,或者插入值(按照一定顺序)会整体移动,效率低
4.1.2、链式存储方式的分析
- 优点:在一定程度上对数组存储方式有优化(比如:插入一个数值节点,只需要插入节点,链接到链表中即可,删除效率也很好)
- 缺点:在进行检索时,效率仍然较低,比如遍历的时候需要从头遍历到查到为止
4.1.3、树存储方式的分析
能提高数据存储,读取效率,比如利用二叉排序树。既可以保证数据的检索速度,同时也可以保证数据的插入,删除,修改速度。
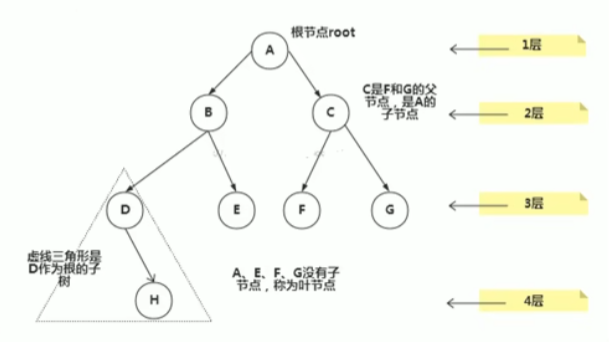
树的常用术语

4.2 二叉树
1.每个节点最多只能有两个子节点的形式叫二叉树,二叉树的子节点又分成左节点和右节点
2.如果二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层,并且节点的总数=2 ^ n - 1 ,n为层数,则我们可以称为满二叉树。
3.如果该二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层后者倒数第二层,而且最后一层的叶子节点都在左边延续,倒数第二层的叶子节点在右边延续,我们可以称之为完全二叉树
4.前序遍历:先输出父节点,再遍历左子树和右子树
5.中序遍历:先遍历左子树,再输出父节点,再遍历右子树
6.后序遍历:先左树,再右树再父节点
这里可以看父节点树的位置来判断
使用CSharp 对于这里的各种顺序的遍历 查找删除
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
|
namespace faithApp
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node node = new Node(1);
Node node1 = new Node(2);
Node node2 = new Node(3);
Node node3 = new Node(4);
Node node4 = new Node(5);
node.leftNode = node1;
node.rightNode = node2;
node2.leftNode = node4;
node2.rightNode = node3;
Tree tree = new Tree();
tree.node = node;
Console.WriteLine("前序遍历");
tree.frontDisplay();
Console.WriteLine("中序遍历");
tree.midDisplay();
Console.WriteLine("后序遍历");
tree.behindDisplay();
var find = tree.frontFind(5);
Console.WriteLine("前序查找找到的节点为:" + find);
var midFind = tree.midFind(5);
Console.WriteLine("中序查找找到的节点为:" + midFind);
var behindFind = tree.behindFind(5);
Console.WriteLine("后序查找找到的节点为:" + behindFind);
Console.WriteLine("start delete ");
tree.deleteNode(5);
tree.frontDisplay();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
class Tree
{
public Node node { get; set; }
public Node frontFind(int val)
{
if (this.node != null)
{
return this.node.frontFind(val);
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
public Node midFind(int val)
{
if (this.node != null)
{
return this.node.midFind(val);
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
public Node behindFind(int val)
{
if (this.node != null)
{
return this.node.behindFind(val);
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
public void frontDisplay()
{
if (this.node != null)
{
this.node.frontDisplay();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("二叉树为null");
}
}
public void midDisplay()
{
if (this.node != null)
{
this.node.midDisplay();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("二叉树为null");
}
}
public void behindDisplay()
{
if (this.node != null)
{
this.node.behindDisplay();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("二叉树为null");
}
}
public void deleteNode(int val)
{
if (this.node != null)
{
if (this.node.val == val)
{
this.node= null;
return;
}
node.deleteNode(val);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("tree is null");
}
}
}
class Node
{
public Node()
{
}
public Node(int val)
{
this.val = val;
}
public int val { get; set; }
public Node leftNode { get; set; }
public Node rightNode { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
return $"节点权为:{val}";
}
public Node frontFind(int val)
{
Console.WriteLine("进入前序查找!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!");
if (this.val == val)
{
return this;
}
Node node = null;
if (this.leftNode != null)
{
node = this.leftNode.frontFind(val);
}
if (node != null)
{
return node;
}
if (this.rightNode != null)
{
node = this.rightNode.frontFind(val);
}
return node;
}
public Node midFind(int val)
{
Console.WriteLine("进入中序查找!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!");
Node node = null;
if (this.leftNode != null)
{
node = this.leftNode.frontFind(val);
}
if (node != null)
{
return node;
}
if (this.val == val)
{
return this;
}
if (this.rightNode != null)
{
node = this.rightNode.frontFind(val);
}
return node;
}
public Node behindFind(int val)
{
Console.WriteLine("进入后序查找!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!");
Node node = null;
if (this.leftNode != null)
{
node = this.leftNode.frontFind(val);
}
if (node != null)
{
return node;
}
if (this.rightNode != null)
{
node = this.rightNode.frontFind(val);
}
if (node != null)
{
return node;
}
if (this.val == val)
{
return this;
}
return node;
}
public void frontDisplay()
{
Console.WriteLine(this.ToString());
if (this.leftNode != null)
{
this.leftNode.frontDisplay();
}
if (this.rightNode != null)
{
this.rightNode.frontDisplay();
}
}
public void midDisplay()
{
if (this.leftNode != null)
{
this.leftNode.midDisplay();
}
Console.WriteLine(this.ToString());
if (this.rightNode != null)
{
this.rightNode.midDisplay();
}
}
public void behindDisplay()
{
if (this.leftNode != null)
{
this.leftNode.behindDisplay();
}
if (this.rightNode != null)
{
this.rightNode.behindDisplay();
}
Console.WriteLine(this.ToString());
}
public void deleteNode(int val)
{
if (this.leftNode !=null && this.leftNode.val == val)
{
this.leftNode = null;
return;
}
if (this.rightNode != null && this.rightNode.val == val)
{
this.rightNode = null;
return;
}
if (this.leftNode != null)
{
this.leftNode.deleteNode(val);
}
if (this.rightNode != null)
{
this.rightNode.deleteNode(val);
}
}
}
}
|
4.3 顺序存储二叉树
二叉树可以和一个有序数组进行转换 前提是这个二叉数组是完全二叉树
1.第n个元素的左子节点为2n+1
2.第n个元素的右子节点为2n+2
3.第n个元素的父节点(n-1)/2
这里的n表示二叉树中的第几个元素(从0开始)